How to calculate the optimal free shipping for you

A challenge that many e-tailers struggle with is shipping and how to price their shipping to customers. To build up levels and try to trigger a more expensive shopping basket, you can use a free shipping limit, among other things. Whether or not free shipping is a hot potato is a hot potato among e-tailers and most would probably have avoided it completely, but if you are now going to get into free shipping, you have to keep your tongue in your mouth.
The big challenge is to find a "just right" level to induce increased purchase. This also presupposes that you have products of which several are needed, and that you have a sufficiently large product range, in order to be able to trigger more lines on the order. There are also techniques where you use discounts as a two-stage rocket before reaching the level where you offer free shipping, but in this example we will focus on only free shipping as a tool.
We want to make more money!
There are several ways to calculate, but in the following examples we start from the current situation and calculate what should be the free shipping limit without cannibalizing current sales. The goal is not only to increase the value of the shopping basket, but also to make more money in the end.
Swedish Priceindx is growing steadily and today has a large number of customers around Europe. The majority since 2006 when the company developed its first services.
Since in the example we have used straight shipping, i.e. we only invoice the shipping, we must first look at what amount we have to increase our shopping cart by to cover the increased cost we have when we offer free shipping.
Shipping cost of SEK 50
Assuming we have a continued 20 percent margin, we need SEK 250 in increased sales value to break even on the free shipping. See the diagram below which increased sales value different margins require to cover SEK 50 in free shipping. We have chosen SEK 50 as a base, then if it is SEK 40, 45 or 50, the respective e-merchants can put it into their own calculations.
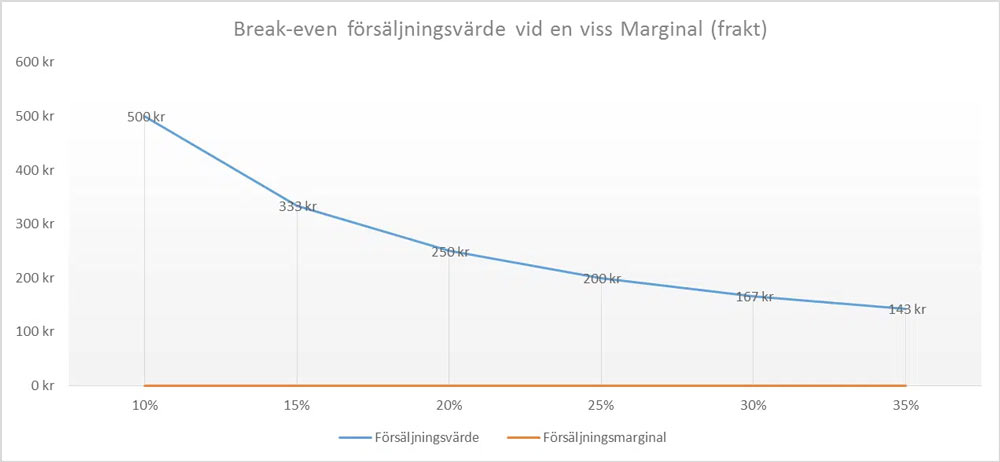
Since the shipping cost is constant (50 kroner), the difference between the different margin steps decreases and the higher the margin, the lower the sales value we need to cover the cost.
No problem with that, and this gives us our second graph below which shows our average value (450 kroner) of the shopping cart in the example with the increased product value we need to cover the free shipping at different margins.
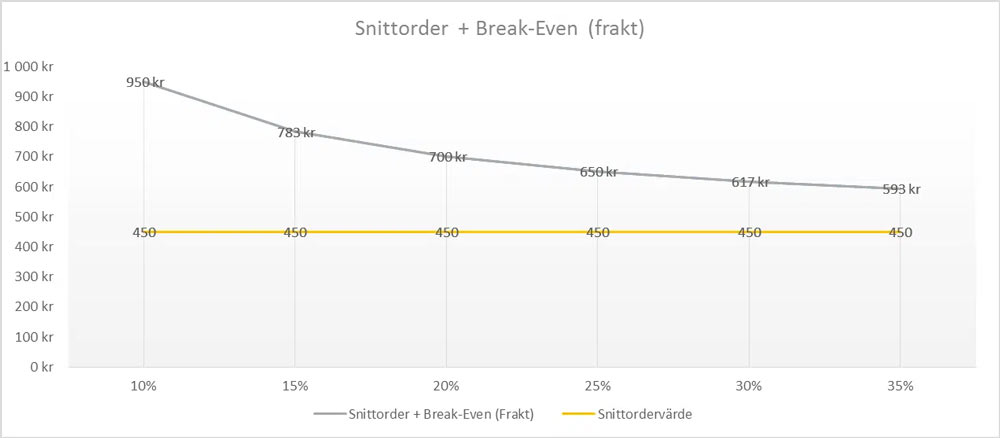
This "limit" corresponds to the current average cart only with an added limit to cover the free shipping. Our goal is to increase the kroner earned, which means that we have to find a suitable level above the above line where we actually make more money.
SEK 700 to cover shipping
To make it easier to trigger the customer to buy, you can try to put the free shipping limit just above a threshold based on both a new accepted shopping cart and a psychologically good price. In our example, the average price per product is SEK 150, and according to the graph above, we need at least SEK 700 to cover our costs.
If we then assume that the new free shipping basket will increase from three products (450 kroner) to five products (450 kroner + 300 kroner), we are up to 750 kroner. If you then throw in the VAT, we are up to SEK 937.
SEK 995 psychologically good
If we choose to round up to a psychologically "good" price, we end up at SEK 995 (including VAT). Then you can discuss whether to round up or down, but since our goal with this exercise is to make more money and increase profitability rather than turnover, it has been rounded up. This corresponds to SEK 796 excluding VAT, i.e. 12 percent more than we need to go plus/minus from our old average basket.
To trigger the customer to add more products with a higher margin, the store can offer several "add on" products that make it easier for the customer to take the step to add more lines to the order. If you focus on high-margin products, you can adjust the free shipping limit downwards, which makes it more attractive.
Additional purchases open up a lower free shipping limit
The graph below shows with the dashed line where the break-even could be if you can raise the margins on the additional purchase by 5 percentage points compared to the average basket. If you succeed in this, the low-margin products are mainly affected, which may also be the ones on which the stores can benefit the most from getting a lower free shipping limit. This is because they are often more competitive.
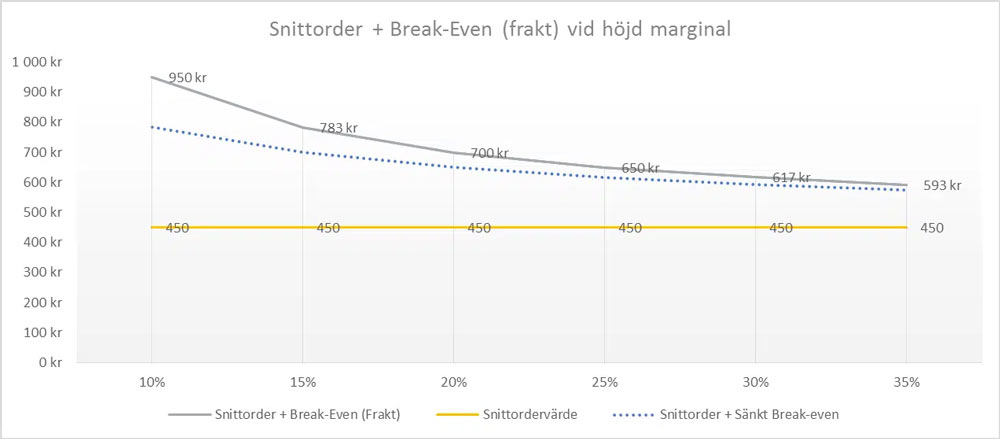
If you screw up properly in the meantime, free shipping can be an excellent tool to increase the order value but also to increase the margin if the "right" add-on products are presented to trigger the customer to get over the limit.
These levels, just like everything else in e-commerce, are very dynamic and change over time, and it is important to follow along and check that you are at the right level both financially but also against your competitors, which these examples do not take into account.
Hope we were able to give you some meat on your legs if you are thinking about entering the free shipping e-commerce. These are not easy calculations, as we have seen when a giant like Komplett had to back down on its free shipping in the past .
Read article at ehandel.se


